This articles explains the basics on how to use MongoDB in Stambia DI.
Please refer to this article to find all the necessary material.
Prerequisites:
- Stambia DI Runtime S17.3.0 or higher
- Stambia DI Designer S18.2.0 or higher
Metadata
Creation
Create a new MongoDB Metadata:
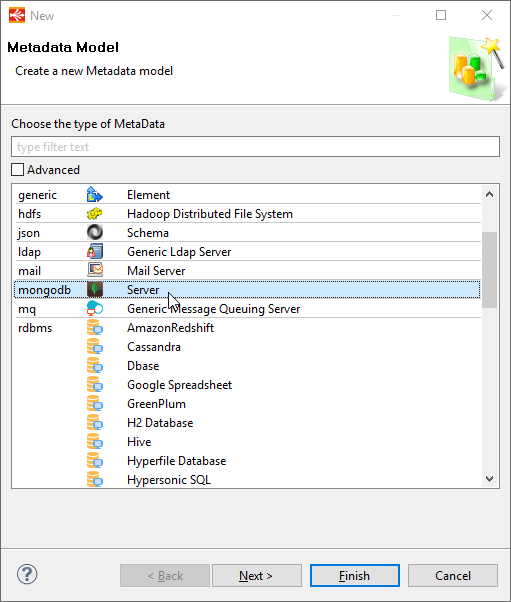
Configure the root node:
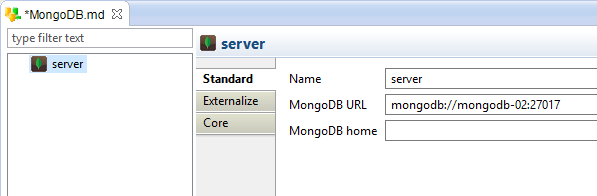
| Property |
Description |
| Name |
Alias/label of the Mongodb server. |
| MongoDB URL |
MongoDB server URL.
mongodb://[<user>:<password>@]<host>:<port>
Some examples:
mongodb://localhost:27017
mongodb://myUser:myPassword@localhost:27017
|
| MongoDB home |
Path to the MongoDB server installation directory.
It is used by the templates importing data through the mongoimport utility.
|
Reverse
Each node of the MongoDB metadata offers the possibility to reverse its structure.
Simply right click on the desired node and choose: Actions > Reverse [All]
-
On the server node: All databases and collections are reversed
-
On a database node: All the collections of the database are reversed
-
On a collection: The collection is reversed
Manual configuration
Database
Add a database by right clicking on the server node and choosing New > Database.
| Property |
Description |
| Name |
Alias/label of the database |
| Database Physical Name |
Physical Name of the database.
It will be used during data and reverse operations.
|
You can reverse all the collections of the database with right click > Actions > Reverse.
Collection
Add a collection by right clicking on a database node and choosing New > Collection.
| Property |
Description |
| Name |
Alias/label of the collection |
| Collection Physical Name |
Physical Name of the collection.
It will be used during data and reverse operations.
|
You can then reverse the collection with right click > Actions > Reverse.
You can alternatively create the collection structure manually by adding its content with right click > New > [...].
MongoDB data Integration
MongoDB collections can be loaded from any database through the 'INTEGRATION Rdbms to MongoDB (crud)' template.
- Create a Mapping
- Drag and drop the target MongoDB collection and the source tables.
- Map your fields as usual.
- Set the 'MongoDB Operation' parameter to the wanted operation.
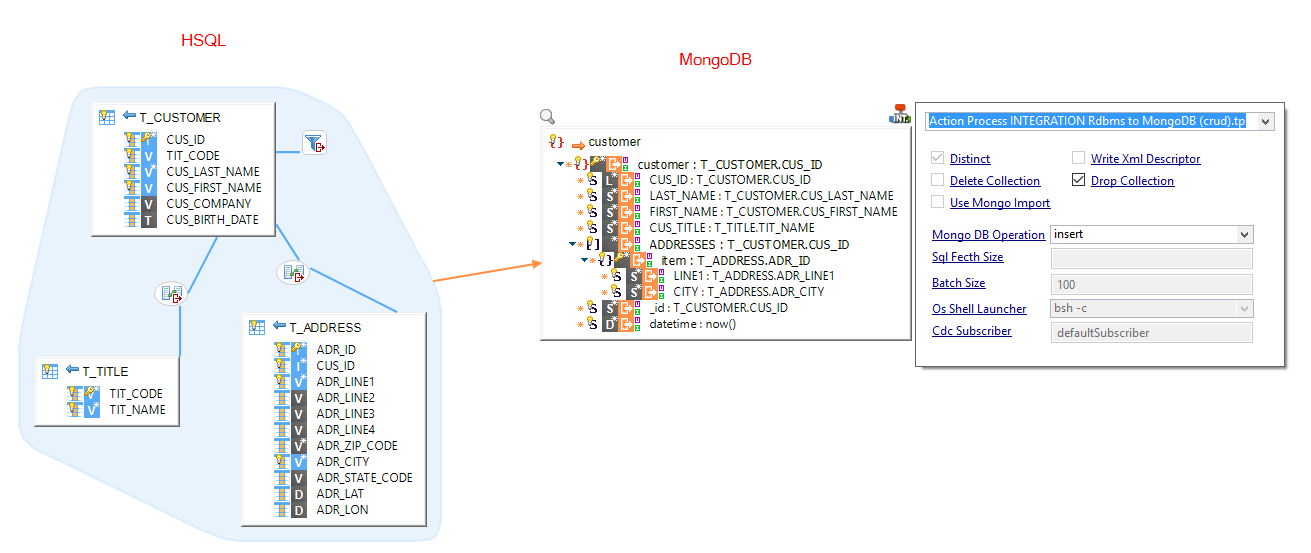
Note: Please refer to the template's internal documentation for more detailed information.
Read data from MongoDB
MongoDB collections can be accessed through the 'INTEGRATION Rdbms to MongoDB (crud)' template to load any database.
To read MongoDB data, you'll need to invoke it from a source to have a repetition key, like you would do for XML files or Web Services.
- Create a Mapping
- Drag and drop:
- The source table that will invoke MongoDB
- The MongoDB collection
- The target table
- Map the root node of the MongoDB collection from the source
- Map your fields to the target table as usual
- Set the 'MongoDB Operation' parameter to the 'get' operation.
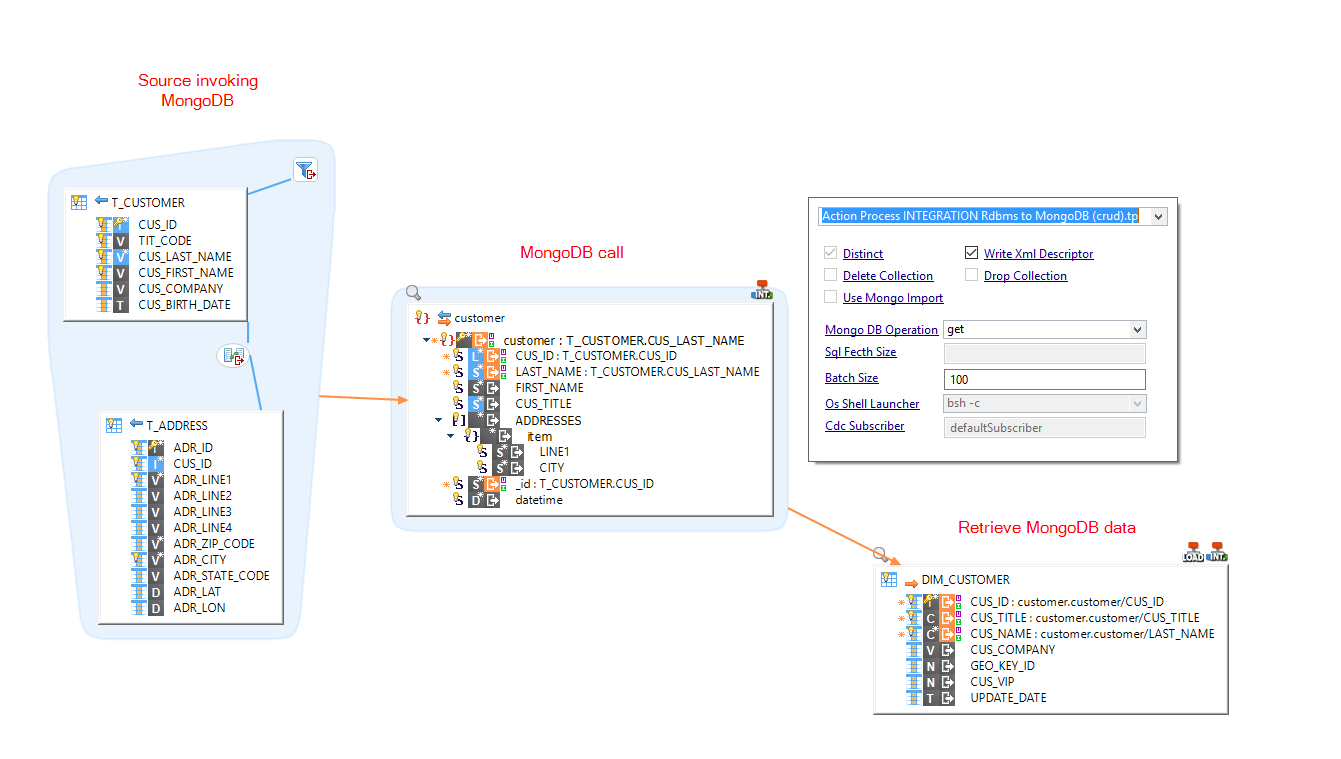
Tip: The source invoking MongoDB here is just used for the repetition key. We are using in our case a temporary in memory table to avoid using a 'real' table just for that. See this article to learn how to accomplish this.
Note: Please refer to the template's internal documentation for more detailed information.




